01. 빈 스코프란?
- 지금까지 우리는 스프링 빈이 “스프링 컨테이너의 시작”과 함께 생성되어서 “스프링 컨테이너가 종료” 될 때까지 유지된다고 학습 하였다
- 이것은 스프링 빈이 기본적으로 싱글톤 스코프로 생성되기 때문이다
- 스코프는 번역 그대로 빈이 존재할 수 있는 범위를 뜻함
01-1. 스프링이 지원하는 다양한 스코프
- 싱글톤
- 기본 스코프, 스프링 컨테이너의 시작과 종료까지 유지되는 스코프
- 프로토타입
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈의 생성과 의존관계 주입까지만 관여, 더는 관리하지 않는 매우 짧은 범위의 스코프
- 웹 관련 스코프
- request : 웹 요청이 들어오고 나갈때 까지 유지되는 스코프
- session : 웹 세션이 생성되고 종료될 때 까지 유지되는 스코프
- application : 웹의 서블릿 컨텍스트와 같은 범위로 유지되는 스코프
빈 스코프는 다음과 같이 지정 가능
컴포넌트 스캔 자동 등록
@Scope("prototype")
@Component
public class HelloBean() { }
수동 등록
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean
PrototypeBean HelloBean() {
return new HelloBean();
}02. 프로토타입 스코프
- 싱글톤 스코프의 빈을 조회하면 스프링 컨테이너는 항상 같은 인스턴스의 스프링 빈을 반환
- 반면 프로토타입 스코프를 스프링 컨테이너에 조회하면 항상 새로운 인스턴스를 생성해 반환
02-1. 싱글톤 빈 요청

- 클라이언트 A, B, C → 싱글톤 스코프 빈 요청 → 스프링 컨테이너
- 스프링 컨테이너는 본인이 관리하던 스프링 빈 반환
- 이후 스프링 컨테이너에 같은 요청이 와도 동일 객체 인스턴스 빈을 반환
02-2. 프로토타입 빈 요청 1

- 클라이언트 A, B, C → 프로토타입 스코프 빈 요청 → 스프링 컨테이너
- 스프링 컨테이너는 이 시점에 프로토타입 빈을 생성하고, 의존관계 주입
02-3. 프로토타입 빈 요청 2

- 스프링 컨테이너는 생성한 프로토타입 빈을 클라이언트에 반환
- 이후에 스프링 컨테이너에 같은 요청이 와도 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈을 반환
정리
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 생성하고, 의존관계 주입, 초기화까지만 처리
- 빈을 반환한 이후 생성된 프로토타입 빈을 관리 안함
- @PreDestroy 같은 종료 메서드 호출안됨
02-4. SingletonTest
package hello.core.scope;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class SingletonTest {
/**
* 싱글톤 스코프 빈은 항상 동일한 인스턴스 객체를 반환 한다
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
void singletonBeanFind() throws Exception {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean bean1 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean bean2 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
System.out.println("bean1 = " + bean1);
System.out.println("bean2 = " + bean2);
System.out.println("Is same instance? bean1 == bean2 => " + (bean1 == bean2)); // true
// 동일한 인스턴스 객체인가?
Assertions.assertThat(bean1).isSameAs(bean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("singleton") // default : singleton
static class SingletonBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println(">>>> SingletonBean.init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println(">>>> SingletonBean.destroy");
}
}
}
- 싱글톤 스코프 테스트코드 작성, 항상 동일한 객체를 반환하는지 테스트 진행
02-5. PrototypeTest
package hello.core.scope;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
public class PrototypeTest {
@Test
void prototypeBeanFind() throws Exception {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("find prototypeBean1");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("find prototypeBean2");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("prototypeBean1 = " + prototypeBean1);
System.out.println("prototypeBean2 = " + prototypeBean2);
assertThat(prototypeBean1).isNotSameAs(prototypeBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("prototype")
//@Component -> ?? -> new Annotation..(PrototypeBean.class) 지정 시 @Component가 달린 것처럼 동작 함
static class PrototypeBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println(">>>> PrototypeBean.init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println(">>>> PrototypeBean.destroy");
}
}
}
- 프로토타입 스코프 테스트 코드 작성, 호출할때마다 새로운 객체를 생성해서 반환
프로토타입 스코프의 경우 항상 새로운 객체를 생성해 반환한다. 위 테스트 코드 실행 후 로그를 살펴보자
17:08:49.086 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory - Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory'
17:08:49.087 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory - Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor'
17:08:49.090 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory - Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor'
find prototypeBean1
>>>> PrototypeBean.init // 새로운 Bean 생성
find prototypeBean2
>>>> PrototypeBean.init // 새로운 Bean 생성
// 객체의 참조 주소가 다름
prototypeBean1 = hello.core.scope.PrototypeTest$PrototypeBean@19c65cdc
prototypeBean2 = hello.core.scope.PrototypeTest$PrototypeBean@74bf1791
17:08:49.215 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext - Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@7133da86, started on Sat Mar 11 17:08:49 KST 2023
- init 메서드가 2번 호출됨
- 반환된 객체가 다른 것 역시 확인 가능
정리
싱글톤
- 싱글톤 빈은 컨테이너 생성 시점에 빈이 생성되고 초기화 메서드가 실행됨
- 싱글톤 빈은 2번 조회해도 동일한 빈을 반환함 (싱글톤)
- 싱글톤 빈은 컨테이너에게 관리 되기에 @Predestroy가 호출됨
프로토타입
- 프로토타입 스코프 빈은 컨테이너에서 빈을 조회할때 빈이 생성되고, 초기화 메서드가 실행됨
- 프로토타입 빈을 2번 조회 했으므로 완전히 다른 빈 생성, 초기화도 2번 실행된 것 확인 가능
- 프로토타입 빈은 컨테이너에게 관리 되지 않기 때문에 @Predestroy가 호출 안됨
03. 프로토타입 스코프 - 싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용 시 문제점
- 프로토타입 스코프 싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용 시 문제점 확인
- 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 스코프 빈을 요청하면 항상 새로운 객체를 생성해 반환한다. 하지만 싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용할때는 의도한대로 잘 동작하지 않으므로 주의해야 한다.
03-1. 프로토타입 빈 직접 요청하는 경우 - 클라이언트 A

- 클라이언트 A는 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈을 요청한다
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 새로 생성해서 반환(x01)한다. 해당 빈의 count 필드 값은 0이다
- 클라이언트는 조회한 프로토타입 빈에 addCount() 를 호출하면서 count 필드를 + 1 한다
- 결과적으로 프로토타입 빈(x01)의 count는 1이 된다
03-2. 프로토타입 빈 직접 요청하는 경우 2 - 클라이언트 B
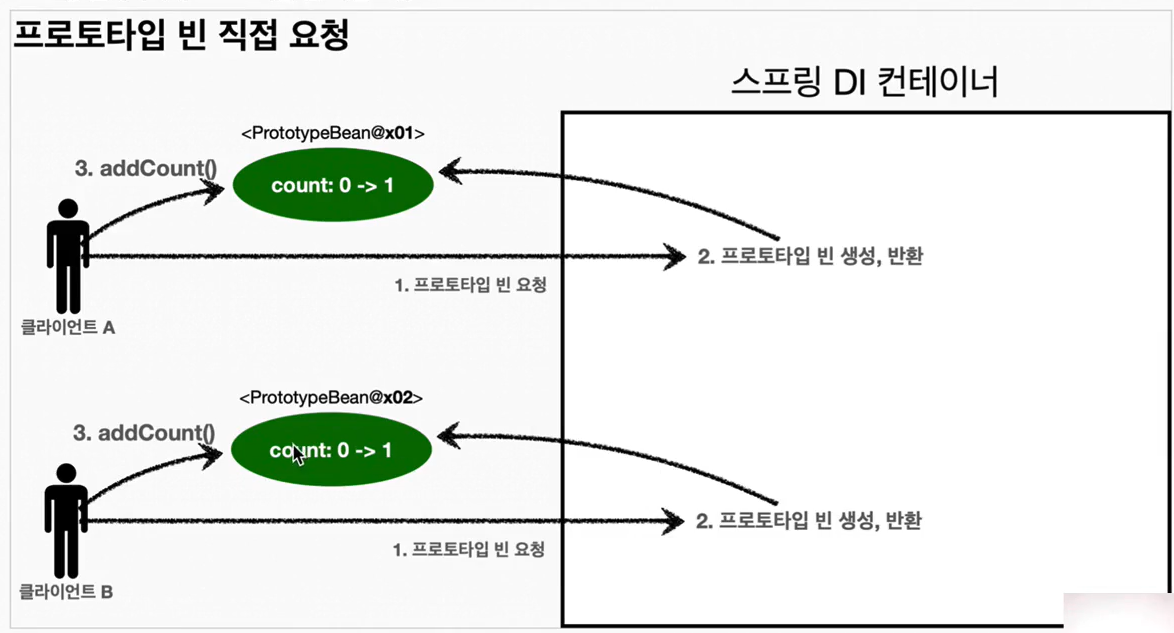
- 클라이언트 B는 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈을 요청한다
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 새로 생성해 반환(x02)한다. 해당 빈의 count 필드 값은 0이다
- 클라이언트는 조회한 프로토타입 빈에 addCount() 를 호출하면서 count 필드를 + 1 한다
- 결과적으로 프로토타입 빈(x02)의 count는 1이 된다
03-3. SingletonWithPrototypeTest1
package hello.core.scope;
...
public class SingletonWithPrototypeTest1 {
@Test
void prototypeFind() throws Exception {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
// 스프링 컨테이너에 prototypeBean 객체 요청(1)
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean1.addCount();
assertThat(prototypeBean1.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
// 스프링 컨테이너에 prototypeBean 객체 요청(2)
// 아래 빈(Bean)은 프로토타입 스코프 빈 이므로 새로운 객체가 생성되어 반환이 된다
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean2.addCount();
assertThat(prototypeBean2.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
private int count = 0;
public void addCount() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.init => " + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.destroy => " + this);
}
}
}03-4. 싱글톤 빈에서 프로토타입 빈 사용 1
이번에는 ClientBean이라는 싱글톤 빈이 의존관계 주입을 통해서 프로토타입 빈을 주입받아서 사용하는 예시
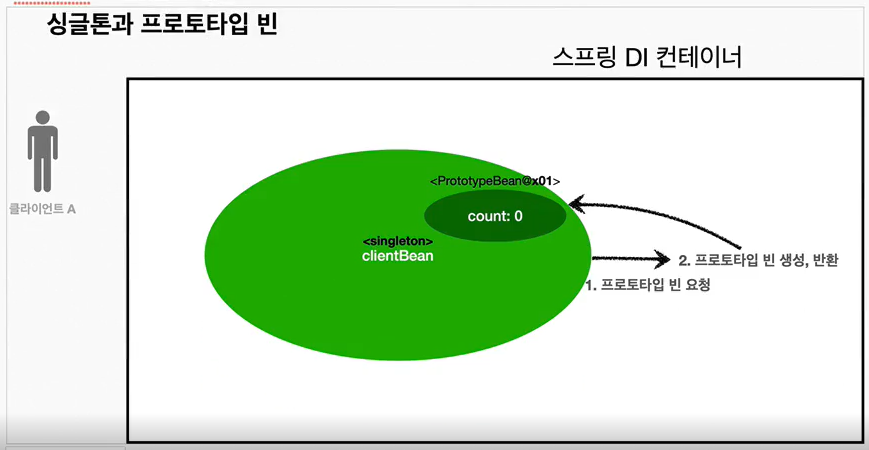
- clientBean은 싱글톤이므로 보통 스프링 컨테이너 생성 시점에 함께 생성되고, 의존관계 주입도 발생함
- clientBean은 의존관계 자동 주입을 사용한다. 주입 시점에 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈(PrototypeBean) 요청
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 생성해서 clientBean에 반환한다. 프로토타입 빈의 count 필드 값은 0
- 이제 clientBean은 프로토타입 빈을 내부 필드에 보관하고 있는다 (정확히 참조값 보관)
03-5. 싱글톤 빈에서 프로토타입 빈 사용 2

- 클라이언트 A는 clientBean을 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 받는다. 싱글톤이므로 항상 같은 clientBean 반환
- 클라이언트 A는 clientBean.logic() 을 호출한다
- clientBean은 prototypeBean의 addCount()를 호출해서 프로토타입 빈의 count를 증가한다 count → 1

03-6. 싱글톤 빈에서 프로토타입 빈 사용 3

- 클라이언트 B는 clientBean을 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 받는다. 싱글톤이므로 항상 같은 clientBean 반환
- 여기서 중요한 부분은, clientBean이 내부에 가지고 있는 프로토타입 빈은 이미 과거에 주입이 끝난 빈이다 주입 시점에 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 프로토타입 빈이 새로 생성된 것이지, 사용 할 때마다 새로 생성되는 것은 아니다!
- 클라이언트 B는 clientBean.logic() 을 호출한다
- clientBean은 prototypeBean의 addCount()를 호출해서 프로토타입 빈의 count를 증가한다 원래 1이었으므로 이제 2가 된다
03-8. SingletonWithPrototypeTest1.singletonClientUsePrototype
package hello.core.scope;
...
public class SingletonWithPrototypeTest1 {
/**
* 단순히 프로토타입 빈을 호출하여 카운트가 각각 1이 되는지 확인하기 위함
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
@DisplayName("프로토타입 스코프 빈 호출 시 카운트 증가 테스트")
void prototypeFind() throws Exception {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean1.addCount();
assertThat(prototypeBean1.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean2.addCount();
assertThat(prototypeBean2.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
}
/**
* 싱글톤 빈 안에 있는 프로토타입 빈이 요청할 때마다 새로 생성되는 것을 원하는 상태
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
@DisplayName("싱글톤 스코프 빈 안에 있는 프로토타입 스코프 빈의 메서드를 호출하여 count가 증가 테스트")
void singletonClientUsePrototype() throws Exception {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ClientBean.class, PrototypeBean.class);
/**
remind
- 싱글톤 스코프는 싱글톤 객체 즉, 동일한 객체를 반환함
- 프로토타입 스코프는 새로운 객체를 생성해 반환
*/
ClientBean clientBean1 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count1 = clientBean1.logic();
assertThat(count1).isEqualTo(1);
ClientBean clientBean2 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count2 = clientBean2.logic();
assertThat(count2).isEqualTo(2);
}
/* 싱글톤 스코프 빈 */
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
private final PrototypeBean prototypeBean; // 생성 시점에 이미 의존 관계 주입이 되어 있다
public ClientBean(PrototypeBean prototypeBean) {
this.prototypeBean = prototypeBean;
}
public int logic() {
prototypeBean.addCount();
return prototypeBean.getCount();
}
}
/* 프로토타입 스코프 빈 */
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
private int count = 0;
public void addCount() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.init => " + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.destroy => " + this);
}
}
}
- 스프링은 일반적으로 싱글톤 빈을 사용하므로 싱글톤 빈이 프로토타입 빈을 사용하게 된다
- 하지만 싱글톤 빈은 생성 시점에만 의존관계 주입을 받기 때문에 프로토타입 빈이 새로 생성되기는 하지만, 싱글톤 빈과 함께 계속 유지되는 것이 문제다
- 지금 원하는건 프로토타입 빈을 주입 시점에만 새로 생성하는게 아니라, 사용할 때마다 새로 생성해서 사용하는 것을 원하는 것이다
참고 : 여러 빈에서 같은 프로토타입 빈을 주입 받으면, 주입 받는 시점에 각각 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성된다.
ex)
clientA, ClientB가 각각 의존관계 주입을 받으면 각각 다른 인스턴스의 프로토타입 빈을 주입 받는다
clientA → prototypeBean@x01
clientB → prototypeBean@x02
물론 사용할때마다 새로 생성되는 것은 아니다
04. 프로토타입 스코프 - 싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용 시 Provider로 문제 해결
- 싱글톤 빈과 프로토타입 빈을 같이 사용할 때, 어떻게 하면 사용할 때 마다 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈을 생성할 수 있을까?
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext ac;
public int logic() {
// 의존관계 주입을 사용하지 않고, 직접 컨테이너 뒤져서 적용하는 느낌
PrototypeBean prototypeBean = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean.addCount();
int count = prototypeBean.getCount();
return count;
}- 위 코드를 실행해보면 ac.getBean()을 통해서 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성되는 것 확인 가능
- 프로토타입 빈은 조회할 때마다 Bean을 새로 생성해서 반환 해주기 때문
- 의존관계를 외부에서 주입(DI) 받는게 아니라, 직접 필요한 의존 관계를 찾는 것을 DL(Dependency Lookup) 의존관계 조회 이라 한다
- 이렇게 스프링 애플리케이션 컨텍스트 전체를 주입받게 되면, 스프링 컨테이너에 종속적인 코드가 되고, 단위 테스트가 어려워진다
- 지금 필요한 기능은 지정한 프로토타입 빈을 컨테이너에서 대신 찾아주는 딱! DL 정도의 기능만 제공하는 무언가가 있으면 됨
스프링은 이미 모든 게 준비되어 있음
04-1. ObjectFactory, ObjectProvider
- 지정한 빈을 컨테이너에서 대신 찾아주는 DL 서비스를 제공하는 것이 바로 ObjectProvider 이다. 참고로 과거에는 ObjectFactory가 있었는데, 여기에 편의 기능을 추가해서 ObjectProvider가 만들어짐.
@Autowired
private ObjectProvider<PrototypeBean> prototypeBeanProvider; // 대신 DL을 수행
public int logic() {
PrototypeBean prototypeBean = prototypeBeanProvider.getObject();
prototypeBean.addCount();
return prototypeBean.getCount();
}
- 실행을 해보면 prototypeBeanProvider.getObject() 을 통해서 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있음
- Spring Container의 DL 대신하는 대리자
- ObjectProvider의 getObject() 를 호출하면 내부에서 스프링 컨테이너를 통해 해당 빈을 찾아서 반환
- 스프링이 제공하는 기능을 사용하지만 기능이 단순하므로 단위테스트를 만들거나 mock 코드를 만들기는 훨씬 쉬워진다.
- ObjectProvider는 지금 딱 필요한 DL 정도의 기능 제공
- 특징
- ObjectFactory
- 기능이 단순, 별도의 라이브러리 필요 없음, 스프링에 의존
- ObjectProvider
- ObjectFactory 상속, 옵션, 스트림 처리 등의 편의 기능이 많고, 별도의 라이브러리 필요 없음, 스프링에 의존
- ObjectFactory
04-2. JSR-330 Provider
- 마지막 방법은 javax.inject.Provider 라는 JSR-330 자바 표준을 사용하는 방법
- 이 방법을 사용하면 javax.inject:javax.inject:1 라이브러리 추가 필요
implementation 'javax.inject:javax.inject:1'
@Autowired
private Provider<PrototypeBean> prototypeBeanProvider; // 대신 DL을 수행
public int logic() {
PrototypeBean prototypeBean = prototypeBeanProvider.get();
prototypeBean.addCount();
return prototypeBean.getCount();
}
- 실행 해보면 provider.get() 을 통해서 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있다
- provider의 get()을 호출하면 내부에서 스프링 컨테이너를 통해 해당 빈을 찾아서 반환
- 자바 표준, 기능 단순, 단위 테스트 mock 코드 만들기 쉬움
- 특징
- get() 하나로 기능 단순
- 별도 라이브러리 필요 없음
- 자바 표준, 스프링 아닌 다른 컨테이너에서도 사용 가능
- 정리
- 프로토타입 빈은 언제 사용할까?
- 매번 사용할 때마다 의존관계 주입이 완료된 새로운 객체 필요 시 사용
- 실무에서는 대부분 싱글톤으로 문제 해결 가능
- 직접 사용할 일이 거의 없음
- 프로토타입 빈은 언제 사용할까?
- @Lookup 어노테이션도 DL 지원
05. 웹 스코프
05-1. 웹 스코프의 특징
- 웹 스코프는 웹 환경에서만 동작한다
- 웹 스코프는 프로토타입과 다르게 스프링이 해당 스코프의 종료시점까지 관리. 따라서 종료 메서드 호출
05-2. 웹 스코프 종류
- request
- HTTP 요청 하나가 들어오고 나갈 때 까지 유지되는 스코프, 각각의 HTTP 요청마다 별도의 빈 인스턴스가 생성되고 관리됨
- session
- HTTP Session과 동일한 생명주기
- application
- 서블릿 컨텍스트(ServletContext)와 동일한 생명주기
- websocket
- 웹 소켓과 동일한 생명주기
세션, 서블릿 컨텍스트, 웹 소켓 같은 용어를 모르는 사람도 존재. 여기서는 request 스코프를 예제로 설명. 나머지도 범위만 다르지 동작 방식은 비슷
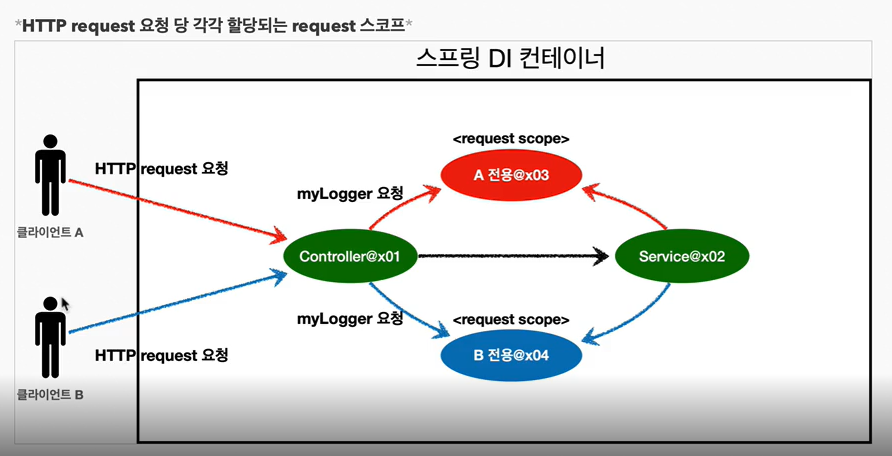
- 클라이언트 A가 요청 → Controller에서 reuqest 스코프와 관련된 객체 조회 → A 전용 객체 반환
- 클라이언트 B가 요청 → Controller에서 reuqest 스코프와 관련된 객체 조회 → B 전용 객체 반환
- HTTP 요청이 들어오고 나갈때까지는 같은 객체(bean)을 반환 및 관리
- A, B에게 각각 다른 Spring Bean이 생성 되어 반환됨
06. request로 스코프 예제 만들기
06-1. build.gradle
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
- web scope 사용을 위해 해당 라이브러리 추가
- spring-boot-starter-web 라이브러리를 사용하면 내장 톰캣 서버를 활용하여 웹 서버와 스프링 실행 시킴
- 스프링 부트의 웹 라이브러리 없다면?
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 기반 애플리케이션 구동
- 스프링 부트의 웹 라이브러리 있다면?
- AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 기반 애플리케이션 구동
06-2. request 스코프 예제 개발
package hello.core.common;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import java.util.UUID;
@Component
@Scope(value = "request")
public class MyLogger {
private String uuid;
private String requestURL;
public void setRequestURL(String requestURL) {
this.requestURL = requestURL;
}
public void log(String message) {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "]" + "[" + requestURL + "]" + message);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
// IOC Container 생성 -> bean 생성 -> bean 의존 관계 주입 -> 초기화 콜백 호출 -> 빈 사용 -> 소멸 콜백 메서드 -> App 종료
uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); // UUID 생성 -> unique 한 값을 받아옴
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean created:" + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean closed:" + this);
}
}
- 동시에 여러 HTTP 요청이 오면 정확히 어떤 요청이 남긴 로그인지 구분이 힘듬
- 이 때 사용하기 좋은게 request scope
- 로그를 출력하기 위한 MyLogger 클래스 생성
- HTTP 요청을 구분하기 위해 uuid를 넣어 로그를 출력
06-3. LogDemoController
package hello.core.web;
import hello.core.common.MyLogger;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Controller
public class LogDemoController {
private final LogDemoService logDemoService;
private final MyLogger myLogger;
@RequestMapping("log-demo")
@ResponseBody
public String logDemo(HttpServletRequest request) {
String requestURL = request.getRequestURL().toString();
myLogger.setRequestURL(requestURL);
myLogger.log("controller test");
logDemoService.logic("testId");
return "OK";
}
}
- HTTP RequestURL을 받아 셋팅 후 로그 출력
- request.getRequestURL() 같은 경우는 필터, 인터셉터에서 공통 처리 가능
06-4. LogDemoService
package hello.core.web;
import hello.core.common.MyLogger;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class LogDemoService {
private MyLogger myLogger;
public void logic(String id) {
myLogger.log("service id = " + id);
}
}
- Service Layer에서 id를 기반으로 로그 출력
06-5. CoreApplication 스프링 구동
2023-04-15 14:30:45.010 INFO 18236 --- [ main] ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener :
Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'debug' enabled.
2023-04-15 14:30:45.038 ERROR 18236 --- [ main] o.s.boot.SpringApplication : Application run failed
org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Error creating bean with name 'logDemoController' defined in file [C:\\workspace-study\\core\\build\\classes\\java\\main\\hello\\core\\web\\LogDemoController.class]: Unsatisfied dependency expressed through constructor parameter 1; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ScopeNotActiveException: Error creating bean with name 'myLogger': Scope 'request' is not active for the current thread; consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: No thread-bound request found: Are you referring to request attributes outside of an actual web request, or processing a request outside of the originally receiving thread? If you are actually operating within a web request and still receive this message, your code is probably running outside of DispatcherServlet: In this case, use RequestContextListener or RequestContextFilter to expose the current request.
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver.createArgumentArray(ConstructorResolver.java:800) ~[spring-beans-5.3.12.jar:5.3.12]
- 스프링 어플리케이션을 실행하면 다음과 같은 ERROR가 발생
- request의 스코프는 HTTP Client의 요청이 있어야 생성이 시작 됨??
- 현재 스프링 애플리케이션이 뜰 때 HTTP Client의 요청을 받는 것은 아님
- 이 때 DL(Provider)를 사용하여 해결이 가능
07. 스코프와 Provider
07-1. LogDemoController
// AS-IS
private final MyLogger myLogger;
// TO-BE
private final ObjectProvider<MyLogger> myLoggerProvider;
- Controller에서 의존성 주입을 해준 myLogger를 ObjectProvider의 제네릭으로 타입으로 지정
- LogDemoService 역시 마찬가지로 해당 소스를 수정 해줌
07-2. 결과 확인
[1e996bfa-cb41-4353-9d31-05f3bc61d75b] request scope bean created:hello.core.common.MyLogger@38910305
[1e996bfa-cb41-4353-9d31-05f3bc61d75b][<http://localhost:8080/log-demo>]controller test
[1e996bfa-cb41-4353-9d31-05f3bc61d75b][<http://localhost:8080/log-demo>]service id = testId
[1e996bfa-cb41-4353-9d31-05f3bc61d75b] request scope bean closed:hello.core.common.MyLogger@38910305
[546273e0-c6ef-4561-a843-b0372b842c09] request scope bean created:hello.core.common.MyLogger@888d14c
[546273e0-c6ef-4561-a843-b0372b842c09][<http://localhost:8080/log-demo>]controller test
[546273e0-c6ef-4561-a843-b0372b842c09][<http://localhost:8080/log-demo>]service id = testId
[546273e0-c6ef-4561-a843-b0372b842c09] request scope bean closed:hello.core.common.MyLogger@888d14c
[89f9de94-a383-4c2f-ad44-05302c473eba] request scope bean created:hello.core.common.MyLogger@574f173
[89f9de94-a383-4c2f-ad44-05302c473eba][<http://localhost:8080/log-demo>]controller test
[89f9de94-a383-4c2f-ad44-05302c473eba][<http://localhost:8080/log-demo>]service id = testId
[89f9de94-a383-4c2f-ad44-05302c473eba] request scope bean closed:hello.core.common.MyLogger@574f173
- 의도한대로 [UUID][http://URL] message 순으로 출력이 됨
- 위 부분은 AOP, 필터, 인터셉터 등등로 처리 가능
- ObjectProvider 덕분에 ObjectProvider.getObject() 를 호출하는 시점까지 request scope 빈 생성 지연 가능
- ObjectProvider.getObject() 를 호출하는 시점에는 HTTP 요청이 진행중이므로 request scope 빈 생성 정상
- 아까는 스프링 올렸을 때 오류 발생
- ObjectProvider.getObject() 를 Controller, Service에서 각각 호출해도 같은 HTTP 요청이면 동일한 빈 반환
08. 스코프와 프록시
08-1. MyLogger
@Component
@Scope(value = "request", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class MyLogger {
...
}
- 여기가 핵심. proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS 를 추가
- 적용 대상이 인터페이스가 아닌 클래스면 TARGET_CLASS 선택
- 적용 대상이 인터페이스면 INTERFACES 선택
- 위 같이 하면 MyLogger의 가짜 프록시 클래스를 생성 후 HTTP request와 상관 없이 프록시 클래스를 다른 빈에 미리 주입해 둘 수 있음
@RequestMapping("log-demo")
@ResponseBody
public String logDemo(HttpServletRequest request) throws InterruptedException {
String requestURL = request.getRequestURL().toString();
System.out.println("myLogger = " + myLogger.getClass()); // prox
...
}
2023-04-15 15:14:41.618 INFO 26172 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2023-04-15 15:14:41.618 INFO 26172 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2023-04-15 15:14:41.619 INFO 26172 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 1 ms
myLogger = class hello.core.common.MyLogger$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$bb0b8675
- print 문을 통해 프록시 객체인 것을 확인
- CGLIB라는 라이브러리로 내 클래스를 상속 받은 가짜 프록시 객체를 만들어서 주입
- @Scope의 proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS 를 설정
- 스프링 컨테이너 CGLIB라는 바이트 코드 조작 라이브러리 사용
- MyLogger 상속받은 가짜 프록시 객체 생성
- 스프링 컨테이너에 myLogger라는 이름으로 진짜 대신에 이 가짜 프록시 객체를 등록
CGLIB의 가짜 프록시 객체는 요청이 오면 그때 내부에서 진짜 빈을 요청하는 로직이 있음
- 가짜 프록시 빈은 내부에 실제 MyLogger(bean)을 찾는 방법을 가지고 있음
- 클라이언트 → myLogger.logic() → 가짜 프록시 빈 호출 → 내부적으로 진짜 빈(myLogger) 로직 호출
- 싱글톤이 아닌, 다른 스코프를 사용할때는 유의하여 사용을 해야함
강의 마무리 고생 했습니다 😀
'Spring Boot > MVC 백엔드 1탄 - Self Study' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring MVC - 핵심 원리 기본] 빈 생명주기 콜백 (0) | 2023.04.25 |
|---|---|
| [Spring MVC - 핵심 원리 기본] 의존관계 자동 주입 (0) | 2023.04.25 |
| [Spring MVC - 핵심 원리 기본]컴포넌트 스캔과 의존관계 자동 주입 (0) | 2023.04.25 |
| [Spring MVC - 핵심 원리 기본] 싱글톤 컨테이너 (0) | 2023.04.25 |
| [Spring MVC - 핵심 원리 기본] 스프링 핵심 원리 이해2 - 객체 지향 원리 적용 (0) | 2023.04.25 |



